Dental hygiene
Dental hygiene is the process of removing plaque and tartar deposits from the surface of the teeth, which helps maintain the health of the teeth and gums. This process involves professional teeth cleaning performed by dentists or dental hygienists and is aimed at preventing periodontal disease and other dental problems.

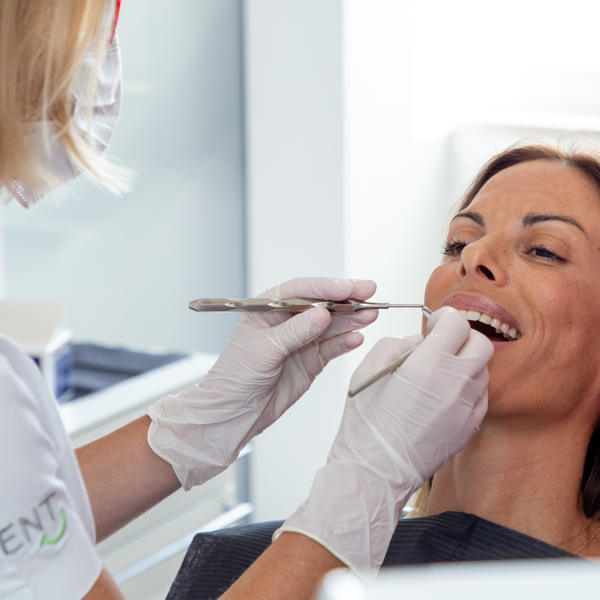
Why is it important?
- Disease prevention - Regular dental hygiene prevents gum disease such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Health maintenance - Helps maintain healthy teeth and gums by removing plaque, bacteria and tartar.
- Aesthetics - Polishing or sandblasting your teeth after removing tartar makes your teeth smoother and brighter, improving their appearance.
- Tooth longevity - Regular hygiene prolongs the lifespan of your teeth and prevents premature tooth loss.
Dental hygiene is essential for maintaining the health of your teeth and gums. It is a series of preventive procedures that effectively remove deposits, prevent tooth decay and gum disease, and ensure the patient's long-term oral health.
FAQ
How often is dental hygiene necessary?
Professional teeth cleaning is recommended every 3, 6 or 12 months, as recommended by a dentist or dental hygienist, depending on the condition of the teeth and gums and the individual needs of the patient.
Why do gums bleed?
Bleeding gums are often a sign of inflammation or irritation of the gums. The most common reasons are:
- Gingivitis – this is a mild inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup; if plaque is not removed regularly by brushing and flossing, the gums become red, swollen and prone to bleeding.
- Periodontitis – if gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more serious infection that can damage the gums and the bone that supports the teeth; periodontitis can cause permanent damage and bleeding of the gums.
- Poor oral hygiene – inadequate or insufficient brushing and flossing can lead to plaque and tartar buildup, which irritates the gums and causes bleeding.
- Using improper brushing or brushing techniques - brushing too hard or using hard bristles can damage your gums and cause them to bleed.
- Hormonal changes - Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make your gums more sensitive, which can lead to bleeding.
- Smoking - Smoking can weaken your immune system and make it harder for your body to fight gum infections, which can lead to bleeding.
- Vitamin deficiencies - A lack of vitamins C and K can cause gum sensitivity and bleeding.
- Certain medications - Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can increase your risk of bleeding gums.
- Stress and a weakened immune system - Stress can weaken your immune system, making your gums more susceptible to infection and inflammation.
How to prevent bleeding gums?
The golden rules are: regular oral hygiene twice a day, correct brushing technique, regular dental checkups, healthy diet, avoiding smoking and managing stress.

"In addition to oral hygiene, prevention is also extremely important. Regular visits to the dentist and dental hygienist are essential to prevent tooth decay, periodontal disease and all the other factors that favor the development of the disease. Experienced hygienists will teach you how to adapt the best oral hygiene routine, because oral health care is an investment in the overall health of an individual."
Tea Kučić, BSc in dental hygiene