30.10.2021
What is periodontitis and why does it appear?
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the supporting tissue of the tooth whose task is to connect the tooth with the jaw bone. Worldwide, an average of 20% to 50% of the population suffers from this disease. One or more related risk factors are responsible for the development of this disease, namely smoking, poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes in women, diabetes, drugs that reduce the flow of saliva in the mouth and stress.
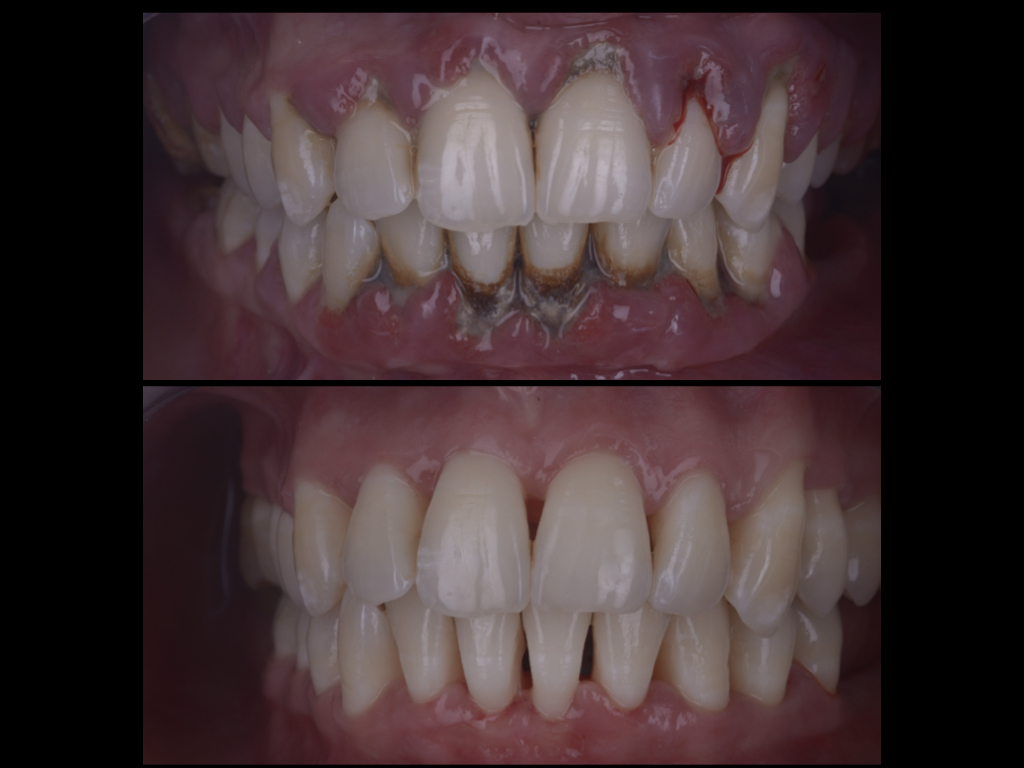
How to recognize this disease?
The disease most often begins as gingivitis, ie inflammation of the gums which is then characterized by redness, swelling and bleeding. If the disease is not treated at this stage it progresses to periodontitis in which an ever-growing tooth pocket is formed. It contains bacteria that cause inflammation of the gums, the ligament that attaches the tooth to the bone and bone. The end result of this inflammation is the irreversible withdrawal of the gums, bones and ligaments and the loss of tooth stability, ie tooth wobble and tooth loss.
The disease can be recognized in the initial stage of gingivitis if redness, swelling and bleeding of the gums during brushing are noticed. As the disease progresses, more and more deposits of bacteria that calcify are created and tartar is formed on the teeth, which is easily noticeable and felt.
How to prevent the development of periodontitis?
The development of periodontitis and further destruction of the supporting tissues of the teeth are prevented in four stages. These phases do not necessarily take place in separate visits to the dentist, but they are a lengthy process that requires changes in some of the patient’s habits, as well as trust and a good relationship between the patient and the dentist.

In the first phase, the dentist finds out from the conversation and the patient’s examination what the cause of this disease is. This phase is also the most important phase in the prevention of periodontitis, because the elimination of the cause also eliminates the disease. If we want to prevent the disease, the patient must change habits.
Cigarette smoking causes less blood supply to the supporting tissues of the teeth and less saliva flow in the mouth, and according to some studies, smoking is the cause of this disease in 42% of patients with periodontitis. Quitting cigarette smoking is a necessary step in preventing periodontitis.
Poor oral hygiene causes the accumulation of bacteria, the formation of plaque and tartar on the teeth and consequently periodontitis. Maintaining oral hygiene in terms of mandatory brushing teeth twice a day, the use of interdental brushes, dental floss, mouthwash is necessary in the prevention of disease. A dentist will educate you on how to properly maintain oral hygiene.
If the cause of this disease is hormonal changes, diabetes or the use of some drugs that reduce the flow of saliva, the dentist, the patient and the family doctor can work together to prevent the development of periodontitis.
The second phase includes professional cleaning of dental plaque performed by a dentist in the office. They are removed with ultrasonic instruments, by polishing the teeth with special pastes, by sandblasting the teeth or by manually scraping the tooth roots (curettage).
In the third phase, the consequences caused by this disease are removed. Depending on the consequences of the disease, this phase includes the removal of caries, endodontic treatment of teeth, prosthetic or implant prosthetic therapy, periodontal surgery.
The fourth phase in treatment involves creating a visit plan and agreeing with the patient on regular checkups and professional teeth cleaning. Adherence to these arrangements is very important in order to maintain the health of the oral cavity and teeth.